FAQ
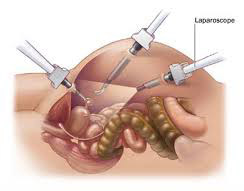
What is laparoscopy?
Laparoscopy is an operation done to look inside your abdomen with a thin instrument called a laparoscope. Through small holes in your tummy, the doctor looks, examines and operates (if needed) without making large cuts.
What are the advantages of a laparoscopic surgery?
In conventional surgery a long incision is made to gain entry into the abdominal cavity and operate. This result in increased post-operative pain, longer stay in hospital, delayed recovery, long and ugly scars, higher chance of wound infection and a higher chance of hernia. The incidence of all these are considerably reduced by a laparoscopic surgery.
What is to be expected after a laparoscopy surgery?
There may be some discomfort in the abdomen for a day or two after laparoscopy due to the presence of some carbon dioxide gas. If the surgery is uneventful, feeding can be started on the same day once the patient has recovered completely from the effects of anesthesia. Before you go home you will be given advice about caring for the surgical wounds and when you will need to come back for a follow-up appointment or to have stitches removed. Complete recovery may take longer if any surgery has been carried out. It is important to follow the advice of your surgeon about physical activity, rest and returning to work.
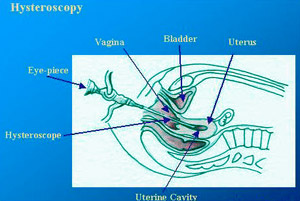
What is a hysteroscopy operation?
A hysteroscopy is an operation done to evaluate the inside of the uterine cavity and if necessary operate on the same.
How exactly is it done?
A narrow telescope with an illuminated lens at its end is introduced in the uterine cavity through the cervix or neck of the womb. For clear vision, the uterine cavity needs to be distended, which is done with gas or some fluid.
Is it a major surgery?
Yes, operations performed through a hysteroscope are major surgeries. Complications may range from anesthetic problems to fluid overload issues. However, hysteroscopy for diagnostic purposes may be performed on an outdoor basis.
When may a hysteroscopy operation be needed?
Hysteroscopy for diagnostic purposes is usually performed to assess the cause of sub fertility or find out the cause of abnormal bleeding. It may also be done to remove polyps, resect septae, release adhesions and retrieve lost IUCDs.
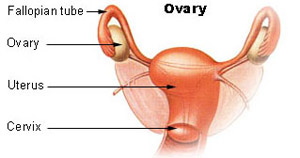
What are ovaries?
Ovaries are female organs, which are like testes in the males. There are two ovaries, right and left.
What are the functions of the ovaries?
Ovaries produce eggs and female hormones, which are required for normal menses till 46 to 50 years of age. At this age, all eggs are finished and no more female hormones are produced. This results in menopause. The woman stops having menses even if she has an intact uterus.

What is HRT?
HRT is Hormone Replacement Treatment. Women take this when there are no female hormones in the body. This can be prescribed after natural menopause or after surgical menopause.
What are the advantages of HRT?
HRT reduces the hot flushes, night sweats, irritability and mood swings associated with menopause. It also reduces the risk of fracture among women after menopause.
How will I know that my menstrual bleeding is heavy?
30% women do not recognize heavy period bleeding. Passing of clots, prolonged bleeding for over a week and flooding are rough indicators of heavy bleeding. The most predictive indicator however is blood hemoglobin estimation. Normal values should be between 12 and 14gm%.
When does heavy bleeding need treatment?
When heavy bleeding is significant enough to cause anemia or severely interferes with one’s quality of life it should be treated. Abnormal heavy bleeding may need investigation and treatment when suspected to be associated with malignancy.
What could be the causes for heavy bleeding?
Hormonal imbalance is one of the most common reasons for heavy bleeding. Besides this, tumors of the uterus, infections, endometriosis, malignancies could also cause heavy bleeding.






